- The Agile Coach
- Agile Manifesto
Agile project management
- Overview
- Project management intro
- Workflow
- Epics, stories, themes
- Epics
- User Stories
- Estimation
- Metrics
- Gantt chart
- Program management vs. project management
- Project baseline
- Continuous improvement
- Lean principles
- 3 pillars of Scrum
- Scrum Board
- Waterfall Methodology
- Velocity in Scrum
- What is Definition of Ready
- Lean vs. agile
- Scrumban
- Lean Methodology
- Sprint backlog
- Burn up chart
- 4 kanban principles
- 4 kanban metrics
- Program vs. Project Manager
- Gantt chart examples
- Definition of done
- Backlog grooming
- Lean process improvement
- Backlog refinement meetings
- Scrum values
- Scope of work
- Scrum tools
- Tools
- Workflow automation software
- Templates
- Task tracker
- Workflow automation
- Status report
- Workflow chart
- Project roadmap
- Project schedule
- Tracking software
- Roadmap tools
- Technology roadmap
- Project scheduling software
- Backlog management tools
- Understanding workflow management strategies
- Workflow examples
- Create project roadmap
- Sprint planning tools
- Sprint demo
- Project Timeline Software
- Top task management tools
- Product backlog vs. sprint backlog
- Top workflow management tools
- Project dependencies
- Task dashboard guide
- Sprint cadence
- Fast tracking
Product Management
- Overview
- Product Roadmaps
- Product Manager
- Tips for new product managers
- Roadmaps
- Tips for presenting product roadmaps
- Requirements
- Product analytics
- Product development
- Remote product management
- Minimal viable product
- Product discovery
- Product specification
- Product development strategy
- Product development software
- New product development process
- Product management KPIs
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Product critique
- Prioritization frameworks
- Product features
- Product management tools
- Product Lifecycle Management
- 9 best roadmap software for teams
- Product launch checklist
- Product strategy
- Product engineering
- Product operations
- Portfolio management
- AI and product management
- Growth product management
- Product metrics
- Product release
- Feature request
- Product launch
- Product planning
- Product launch event
- Value Stream Management
- DevOps
Agile tutorials
- Overview
- Jira and Confluence sprint refinement
- How to do scrum with Jira
- Learn kanban with Jira
- Learn how to use Epics in Jira
- Learn how to create an agile board in Jira
- Learn how to use sprints in Jira
- Learn Versions with Jira
- Learn Issues with Jira
- Learn burndown charts with Jira
- Auto-create sub-tasks and update fields in Jira
- How to automatically assign issues with Jira Automation
- How to sync epics stories with Jira Automation
- Automatically escalate overdue issues in Jira
About the Agile Coach
- All articles
The complete guide to product planning: Benefits and best practices
By Atlassian
By Atlassian
Turn ideas into reality with the free product roadmap template
Communicate and align your product strategy with stakeholders using customizable, interactive roadmaps.
Successful products don't just happen by chance. They result from careful, strategic product planning that guides teams from concept to market launch.
Strong product planning is the foundation for innovation, helping teams prioritize the right ideas, align on goals, and move from brainstorming to execution with clarity and confidence. Without a clear plan, even the best ideas can lose momentum or miss the mark with customers.
This guide will cover the essential steps of effective product planning, its benefits, and best practices to help you build products that resonate with your customers.
What is product planning?
Product planning is the process of conceptualizing, developing, and managing a product throughout its lifecycle. It ensures your product meets market demands while aligning with business objectives. Effective product planning helps teams identify opportunities, mitigate risks, establish clear goals, and create a roadmap for execution.
A well-defined new product planning approach is essential for companies that want to innovate and stay competitive. The process ensures that all resources are allocated efficiently, team members know their tasks, and they can work toward a shared vision.
Key steps of product planning
A successful product planning process follows several essential steps to guide teams from ideation to launch. While the approach may vary depending on your industry, product type, and organizational structure, these fundamental steps provide a framework for bringing successful products to market:
Ideate product concepts
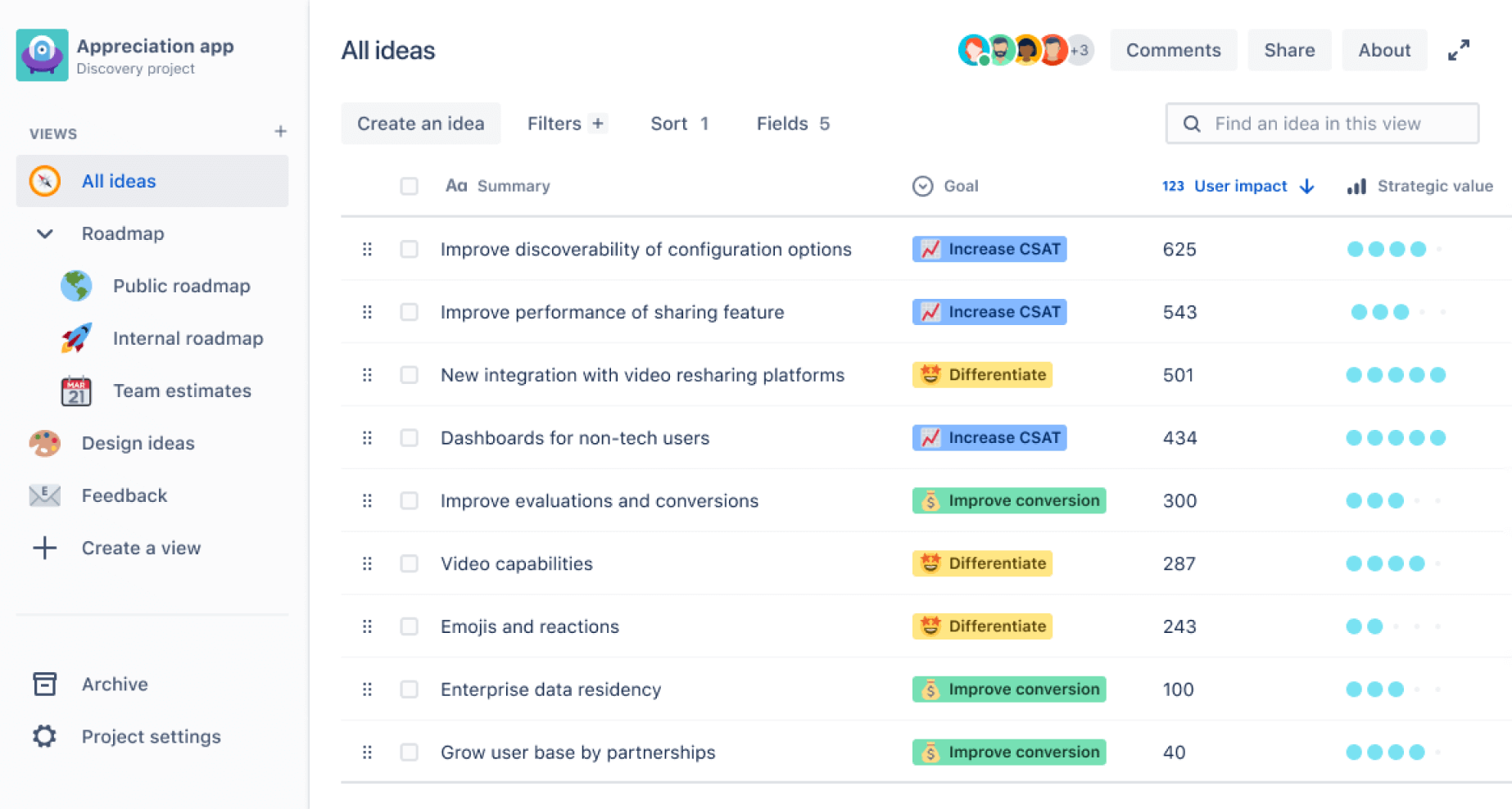
The first step in product planning is generating and refining ideas. This creative phase involves brainstorming sessions where cross-functional teams share ideas without judgment, customer feedback analysis to identify pain points and opportunities, and gap analysis to find unmet needs in the market. Design thinking workshops put the user at the center of ideation, while competitive research helps analyze what competitors offer and identify opportunities to differentiate.
During this phase, it is essential to create an environment where innovative ideas can flourish while maintaining alignment with your overall product strategy.
Conduct market research and analysis
Once you have potential concepts, thorough market research helps validate assumptions and refine ideas. Customer interviews and surveys directly engage potential users to understand their needs, while market sizing determines the potential audience and opportunity. Competitor analysis identifies direct and indirect competitors along with their strengths and weaknesses.
Analyzing industry trends reveals emerging technologies and market directions, and examining regulatory considerations helps you identify compliance issues that might impact development.
This research-driven approach is central to product discovery, helping teams validate that they're solving the right problems for the right audience.
Define product vision and goals
With market insights in hand, the next step is establishing a clear vision and concrete goals. Creating a vision statement provides a compelling description of the product's goals. Defining strategic objectives shows how the product supports broader business goals. Identifying and setting success metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and articulating a value proposition clearly communicates the unique benefits your product will deliver.
This vision is the north star for the entire team throughout the product development process, ensuring everyone understands what they're working on and why they're doing it.
Create product specifications
Product specifications translate your vision into detailed requirements. Feature requirements document the specific capabilities the product must have, while technical specifications define the technologies, integrations, and standards to be used. User stories create detailed scenarios describing how users will interact with the product, and acceptance criteria establish clear conditions that must be met for features to be considered complete.
These specifications serve as a blueprint for development, helping teams understand what needs to be built and how success will be measured.
Develop product roadmap
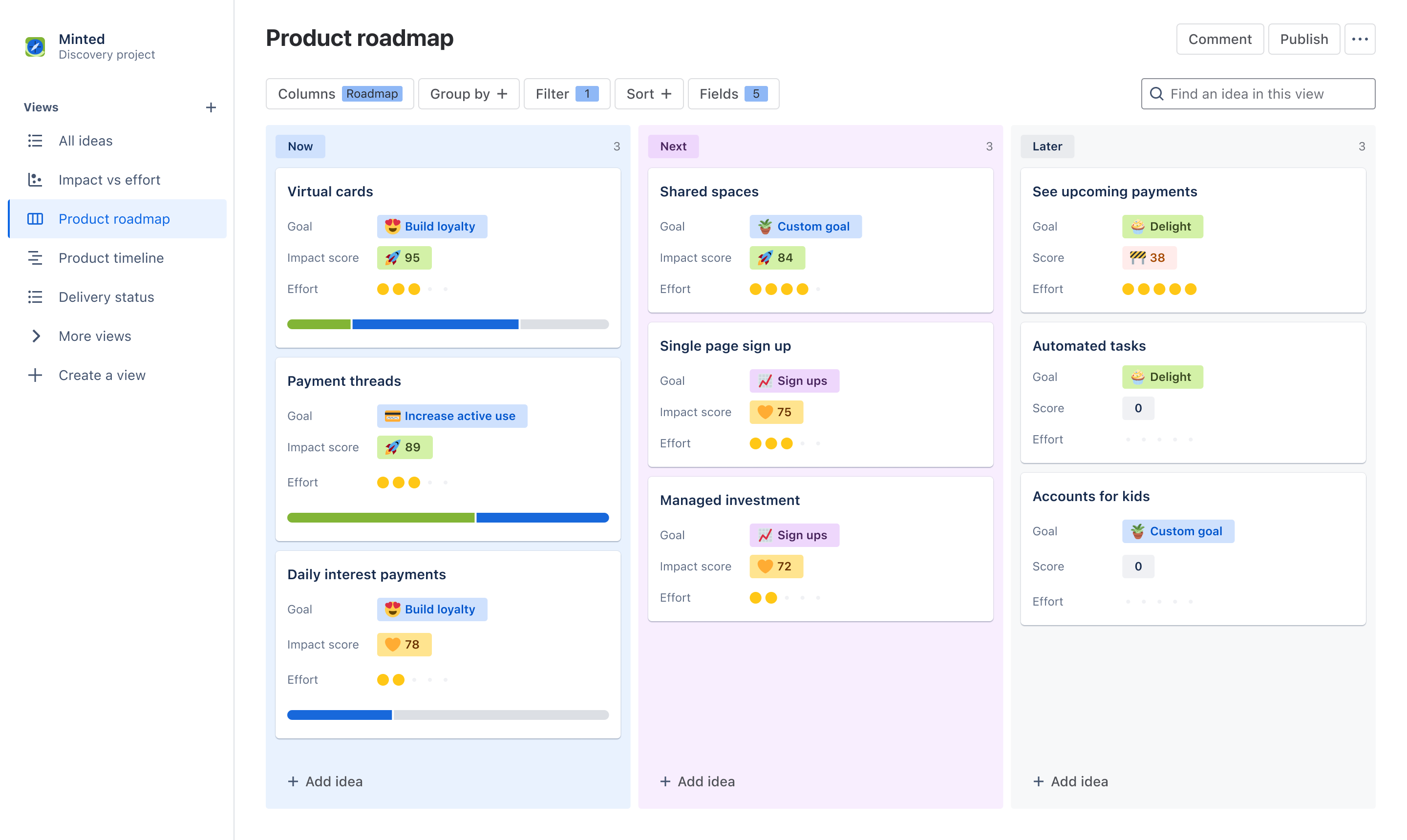
Product roadmaps outline the journey from concept to launch. Feature prioritization determines which capabilities are must-haves versus nice-to-haves, while timeline development creates realistic schedules for development and release. Resource allocation identifies the team members, budget, and tools needed, and milestone definition establishes key checkpoints to measure progress.
Effective roadmaps balance ambition with reality, giving teams a clear, understandable path forward while staying flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances. Agile roadmaps are especially helpful for teams working in dynamic environments.
Check out our product roadmap template for guidance on creating effective roadmaps for your products.
Design and test prototypes
Prototyping validates concepts before significant resources are invested in development. Teams create low-fidelity mockups like simple sketches or wireframes to test basic concepts, then develop interactive prototypes with clickable models to test user workflows. User testing gathers feedback from potential customers on the prototype, allowing teams to iterate and refine the design based on user input and insights.
Designing and testing prototypes allows teams to validate that the planned product features will effectively meet user needs, reducing the risk of building something customers don't want.
Launch product
The final stage of the product planning process is bringing your product to market. Developing a comprehensive go-to-market strategy covers marketing, sales, and distribution approaches. Establishing pricing strategies should reflect value and market positioning. Preparing product launch communication includes messaging for customers, stakeholders, and the market. Support planning ensures customer service teams are fully prepared to assist users.
A successful launch requires close coordination across marketing, sales, product development, and customer support teams to ensure a smooth introduction to the market. For a comprehensive approach to successfully launching your product, refer to Atlassian's product launch checklist.
Benefits of product planning
Investing time and resources in thorough product planning delivers numerous advantages, such as:
Risk reduction: Identifying potential issues early when they're less costly to address.
Resource optimization: Allocating budget, time, and talent more efficiently.
Improved product-market fit: Creating solutions that genuinely address customer needs.
Enhanced collaboration: Fostering alignment across departments and stakeholders.
Faster time-to-market: Reducing delays through clear direction and expectations.
Better decision-making: Providing a framework for evaluating opportunities and trade-offs.
Increased innovation: Creating space for creative solutions within a structured process.
Organizations practicing agile product management find that good planning paradoxically enables greater flexibility, as teams can adapt to changes while maintaining alignment with strategic objectives.
Examples of product planning
Different organizations approach product planning in ways that reflect their industry, size, and culture. Let's take a look at a few examples of how it works in practice:
Enterprise software company: A large software company developing a new customer relationship management (CRM) tool might begin with extensive market research and competitor analysis. Their product planning would include detailed technical specifications, integration requirements, and a phased rollout strategy spanning 12-18 months. Cross-functional teams would work together to ensure the product meets complex enterprise needs while maintaining security and compliance standards.
Consumer electronics startup: A startup creating a new wearable fitness device might take a more agile approach. They might begin with a minimum viable product (MVP) focused on core functionality. Their product planning would emphasize rapid prototyping, user testing, and iterative development cycles. The team might use a condensed timeline of 4-6 months to get to market quickly, with plans to add features based on initial user feedback.
Food and beverage brand: A food company launching a new line of organic snacks would focus its product planning on recipe development, nutritional analysis, packaging design, and distribution strategies. Market testing would be crucial, with focus groups sampling products and providing feedback before full-scale production. Their timeline might be structured around seasonal buying patterns and retail cycles.
Each example demonstrates how product planning can be adapted to different businesses while maintaining the core principles of user-centered design, strategic alignment, and careful execution planning.
Best practices for effective product planning
Follow these best practices to enhance the impact of your project planning efforts:
Stay customer-focused: Always ground decisions in user needs and feedback.
Embrace flexibility: Be willing to adapt plans as you gather new information.
Prioritize ruthlessly: Focus on features that deliver the most value to users and the business.
Maintain clear documentation: Ensure everyone can access and understand the plan.
Foster cross-functional collaboration: Include perspectives from marketing, sales, support, and development.
Use data to drive decisions: Back assumptions with research and metrics whenever possible.
Plan for post-launch: Include strategies for monitoring performance and gathering feedback.
Consider the entire product lifecycle: Think beyond your product launch. Consider ongoing support, updates, and eventual retirement.
These practices help teams navigate the challenges of product life cycle management while focusing on delivering exceptional user experiences.
Optimize product planning with Jira Product Discovery
Jira Product Discovery streamlines the planning process by providing a centralized platform for managing ideas, prioritizing features, and promoting cross-team collaboration. Its purpose-built features support every phase of your product planning journey:
List view for organizing and tracking product ideas and requirements
Custom fields for prioritization that help teams make data-driven decisions
Insights functionality that supports planning with research and feedback integration
Board and timeline views for intuitive roadmapping
Goals integration that maps plans directly to company objectives
When combined with other product development software, Jira Product Discovery creates a seamless workflow from initial concept to delivery.
Confluence further enhances product planning by providing collaborative spaces where teams can document research findings, create detailed specifications, and develop comprehensive strategy documents. Its integration with Jira ensures that plans and execution remain synchronized throughout development.
- The Agile Coach
- Agile Manifesto
Agile project management
- Overview
- Project management intro
- Workflow
- Epics, stories, themes
- Epics
- User Stories
- Estimation
- Metrics
- Gantt chart
- Program management vs. project management
- Project baseline
- Continuous improvement
- Lean principles
- 3 pillars of Scrum
- Scrum Board
- Waterfall Methodology
- Velocity in Scrum
- What is Definition of Ready
- Lean vs. agile
- Scrumban
- Lean Methodology
- Sprint backlog
- Burn up chart
- 4 kanban principles
- 4 kanban metrics
- Program vs. Project Manager
- Gantt chart examples
- Definition of done
- Backlog grooming
- Lean process improvement
- Backlog refinement meetings
- Scrum values
- Scope of work
- Scrum tools
- Tools
- Workflow automation software
- Templates
- Task tracker
- Workflow automation
- Status report
- Workflow chart
- Project roadmap
- Project schedule
- Tracking software
- Roadmap tools
- Technology roadmap
- Project scheduling software
- Backlog management tools
- Understanding workflow management strategies
- Workflow examples
- Create project roadmap
- Sprint planning tools
- Sprint demo
- Project Timeline Software
- Top task management tools
- Product backlog vs. sprint backlog
- Top workflow management tools
- Project dependencies
- Task dashboard guide
- Sprint cadence
- Fast tracking
Product Management
- Overview
- Product Roadmaps
- Product Manager
- Tips for new product managers
- Roadmaps
- Tips for presenting product roadmaps
- Requirements
- Product analytics
- Product development
- Remote product management
- Minimal viable product
- Product discovery
- Product specification
- Product development strategy
- Product development software
- New product development process
- Product management KPIs
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Product critique
- Prioritization frameworks
- Product features
- Product management tools
- Product Lifecycle Management
- 9 best roadmap software for teams
- Product launch checklist
- Product strategy
- Product engineering
- Product operations
- Portfolio management
- AI and product management
- Growth product management
- Product metrics
- Product release
- Feature request
- Product launch
- Product planning
- Product launch event
- Value Stream Management
- DevOps
Agile tutorials
- Overview
- Jira and Confluence sprint refinement
- How to do scrum with Jira
- Learn kanban with Jira
- Learn how to use Epics in Jira
- Learn how to create an agile board in Jira
- Learn how to use sprints in Jira
- Learn Versions with Jira
- Learn Issues with Jira
- Learn burndown charts with Jira
- Auto-create sub-tasks and update fields in Jira
- How to automatically assign issues with Jira Automation
- How to sync epics stories with Jira Automation
- Automatically escalate overdue issues in Jira
About the Agile Coach
- All articles
The complete guide to product planning: Benefits and best practices
By Atlassian
By Atlassian
Turn ideas into reality with the free product roadmap template
Communicate and align your product strategy with stakeholders using customizable, interactive roadmaps.
Successful products don't just happen by chance. They result from careful, strategic product planning that guides teams from concept to market launch.
Strong product planning is the foundation for innovation, helping teams prioritize the right ideas, align on goals, and move from brainstorming to execution with clarity and confidence. Without a clear plan, even the best ideas can lose momentum or miss the mark with customers.
This guide will cover the essential steps of effective product planning, its benefits, and best practices to help you build products that resonate with your customers.
What is product planning?
Product planning is the process of conceptualizing, developing, and managing a product throughout its lifecycle. It ensures your product meets market demands while aligning with business objectives. Effective product planning helps teams identify opportunities, mitigate risks, establish clear goals, and create a roadmap for execution.
A well-defined new product planning approach is essential for companies that want to innovate and stay competitive. The process ensures that all resources are allocated efficiently, team members know their tasks, and they can work toward a shared vision.
Key steps of product planning
A successful product planning process follows several essential steps to guide teams from ideation to launch. While the approach may vary depending on your industry, product type, and organizational structure, these fundamental steps provide a framework for bringing successful products to market:
Ideate product concepts

The first step in product planning is generating and refining ideas. This creative phase involves brainstorming sessions where cross-functional teams share ideas without judgment, customer feedback analysis to identify pain points and opportunities, and gap analysis to find unmet needs in the market. Design thinking workshops put the user at the center of ideation, while competitive research helps analyze what competitors offer and identify opportunities to differentiate.
During this phase, it is essential to create an environment where innovative ideas can flourish while maintaining alignment with your overall product strategy.
Conduct market research and analysis
Once you have potential concepts, thorough market research helps validate assumptions and refine ideas. Customer interviews and surveys directly engage potential users to understand their needs, while market sizing determines the potential audience and opportunity. Competitor analysis identifies direct and indirect competitors along with their strengths and weaknesses.
Analyzing industry trends reveals emerging technologies and market directions, and examining regulatory considerations helps you identify compliance issues that might impact development.
This research-driven approach is central to product discovery, helping teams validate that they're solving the right problems for the right audience.
Define product vision and goals
With market insights in hand, the next step is establishing a clear vision and concrete goals. Creating a vision statement provides a compelling description of the product's goals. Defining strategic objectives shows how the product supports broader business goals. Identifying and setting success metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and articulating a value proposition clearly communicates the unique benefits your product will deliver.
This vision is the north star for the entire team throughout the product development process, ensuring everyone understands what they're working on and why they're doing it.
Create product specifications
Product specifications translate your vision into detailed requirements. Feature requirements document the specific capabilities the product must have, while technical specifications define the technologies, integrations, and standards to be used. User stories create detailed scenarios describing how users will interact with the product, and acceptance criteria establish clear conditions that must be met for features to be considered complete.
These specifications serve as a blueprint for development, helping teams understand what needs to be built and how success will be measured.
Develop product roadmap

Product roadmaps outline the journey from concept to launch. Feature prioritization determines which capabilities are must-haves versus nice-to-haves, while timeline development creates realistic schedules for development and release. Resource allocation identifies the team members, budget, and tools needed, and milestone definition establishes key checkpoints to measure progress.
Effective roadmaps balance ambition with reality, giving teams a clear, understandable path forward while staying flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances. Agile roadmaps are especially helpful for teams working in dynamic environments.
Check out our product roadmap template for guidance on creating effective roadmaps for your products.
Design and test prototypes
Prototyping validates concepts before significant resources are invested in development. Teams create low-fidelity mockups like simple sketches or wireframes to test basic concepts, then develop interactive prototypes with clickable models to test user workflows. User testing gathers feedback from potential customers on the prototype, allowing teams to iterate and refine the design based on user input and insights.
Designing and testing prototypes allows teams to validate that the planned product features will effectively meet user needs, reducing the risk of building something customers don't want.
Launch product
The final stage of the product planning process is bringing your product to market. Developing a comprehensive go-to-market strategy covers marketing, sales, and distribution approaches. Establishing pricing strategies should reflect value and market positioning. Preparing product launch communication includes messaging for customers, stakeholders, and the market. Support planning ensures customer service teams are fully prepared to assist users.
A successful launch requires close coordination across marketing, sales, product development, and customer support teams to ensure a smooth introduction to the market. For a comprehensive approach to successfully launching your product, refer to Atlassian's product launch checklist.
Benefits of product planning
Investing time and resources in thorough product planning delivers numerous advantages, such as:
Risk reduction: Identifying potential issues early when they're less costly to address.
Resource optimization: Allocating budget, time, and talent more efficiently.
Improved product-market fit: Creating solutions that genuinely address customer needs.
Enhanced collaboration: Fostering alignment across departments and stakeholders.
Faster time-to-market: Reducing delays through clear direction and expectations.
Better decision-making: Providing a framework for evaluating opportunities and trade-offs.
Increased innovation: Creating space for creative solutions within a structured process.
Organizations practicing agile product management find that good planning paradoxically enables greater flexibility, as teams can adapt to changes while maintaining alignment with strategic objectives.
Examples of product planning
Different organizations approach product planning in ways that reflect their industry, size, and culture. Let's take a look at a few examples of how it works in practice:
Enterprise software company: A large software company developing a new customer relationship management (CRM) tool might begin with extensive market research and competitor analysis. Their product planning would include detailed technical specifications, integration requirements, and a phased rollout strategy spanning 12-18 months. Cross-functional teams would work together to ensure the product meets complex enterprise needs while maintaining security and compliance standards.
Consumer electronics startup: A startup creating a new wearable fitness device might take a more agile approach. They might begin with a minimum viable product (MVP) focused on core functionality. Their product planning would emphasize rapid prototyping, user testing, and iterative development cycles. The team might use a condensed timeline of 4-6 months to get to market quickly, with plans to add features based on initial user feedback.
Food and beverage brand: A food company launching a new line of organic snacks would focus its product planning on recipe development, nutritional analysis, packaging design, and distribution strategies. Market testing would be crucial, with focus groups sampling products and providing feedback before full-scale production. Their timeline might be structured around seasonal buying patterns and retail cycles.
Each example demonstrates how product planning can be adapted to different businesses while maintaining the core principles of user-centered design, strategic alignment, and careful execution planning.
Best practices for effective product planning
Follow these best practices to enhance the impact of your project planning efforts:
Stay customer-focused: Always ground decisions in user needs and feedback.
Embrace flexibility: Be willing to adapt plans as you gather new information.
Prioritize ruthlessly: Focus on features that deliver the most value to users and the business.
Maintain clear documentation: Ensure everyone can access and understand the plan.
Foster cross-functional collaboration: Include perspectives from marketing, sales, support, and development.
Use data to drive decisions: Back assumptions with research and metrics whenever possible.
Plan for post-launch: Include strategies for monitoring performance and gathering feedback.
Consider the entire product lifecycle: Think beyond your product launch. Consider ongoing support, updates, and eventual retirement.
These practices help teams navigate the challenges of product life cycle management while focusing on delivering exceptional user experiences.
Optimize product planning with Jira Product Discovery
Jira Product Discovery streamlines the planning process by providing a centralized platform for managing ideas, prioritizing features, and promoting cross-team collaboration. Its purpose-built features support every phase of your product planning journey:
List view for organizing and tracking product ideas and requirements
Custom fields for prioritization that help teams make data-driven decisions
Insights functionality that supports planning with research and feedback integration
Board and timeline views for intuitive roadmapping
Goals integration that maps plans directly to company objectives
When combined with other product development software, Jira Product Discovery creates a seamless workflow from initial concept to delivery.
Confluence further enhances product planning by providing collaborative spaces where teams can document research findings, create detailed specifications, and develop comprehensive strategy documents. Its integration with Jira ensures that plans and execution remain synchronized throughout development.
Recommended for you
Templates
Ready-made Jira templates
Browse our library of custom Jira templates for various teams, departments, and workflows.
Product guide
A comprehensive introduction to Jira
Use this step-by-step guide to discover essential features and the best practices to maximize your productivity.
Git Guide
Understanding the Basics of Git
From beginners to advanced experts, use this guide to Git to learn the basics with helpful tutorials and tips.