- The Agile Coach
- Agile Manifesto
Agile project management
- Overview
- Project management intro
- Workflow
- Epics, stories, themes
- Epics
- User Stories
- Estimation
- Metrics
- Gantt chart
- Program management vs. project management
- Project baseline
- Continuous improvement
- Lean principles
- 3 pillars of Scrum
- Scrum Board
- Waterfall Methodology
- Velocity in Scrum
- What is Definition of Ready
- Lean vs. agile
- Scrumban
- Lean Methodology
- Sprint backlog
- Burn up chart
- 4 kanban principles
- 4 kanban metrics
- Program vs. Project Manager
- Gantt chart examples
- Definition of done
- Backlog grooming
- Lean process improvement
- Backlog refinement meetings
- Scrum values
- Scope of work
- Scrum tools
- Tools
- Workflow automation software
- Templates
- Task tracker
- Workflow automation
- Status report
- Workflow chart
- Project roadmap
- Project schedule
- Tracking software
- Roadmap tools
- Technology roadmap
- Project scheduling software
- Backlog management tools
- Understanding workflow management strategies
- Workflow examples
- Create project roadmap
- Sprint planning tools
- Sprint demo
- Project Timeline Software
- Top task management tools
- Product backlog vs. sprint backlog
- Top workflow management tools
- Project dependencies
- Task dashboard guide
- Sprint cadence
- Fast tracking
Product Management
- Overview
- Product Roadmaps
- Product Manager
- Tips for new product managers
- Roadmaps
- Tips for presenting product roadmaps
- Requirements
- Product analytics
- Product development
- Remote product management
- Minimal viable product
- Product discovery
- Product specification
- Product development strategy
- Product development software
- New product development process
- Product management KPIs
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Product critique
- Prioritization frameworks
- Product features
- Product management tools
- Product Lifecycle Management
- 9 best roadmap software for teams
- Product launch checklist
- Product strategy
- Product engineering
- Product operations
- Portfolio management
- AI and product management
- Growth product management
- Product metrics
- Product release
- Feature request
- Product launch
- Product planning
- Product launch event
- Value Stream Management
- DevOps
Agile tutorials
- Overview
- Jira and Confluence sprint refinement
- How to do scrum with Jira
- Learn kanban with Jira
- Learn how to use Epics in Jira
- Learn how to create an agile board in Jira
- Learn how to use sprints in Jira
- Learn Versions with Jira
- Learn Issues with Jira
- Learn burndown charts with Jira
- Auto-create sub-tasks and update fields in Jira
- How to automatically assign issues with Jira Automation
- How to sync epics stories with Jira Automation
- Automatically escalate overdue issues in Jira
About the Agile Coach
- All articles
Agile Project Management - What is it and how to get started?
How agile project management can work for your software team

By Claire Drumond
By Claire Drumond
Claire Drumond is a marketing strategist, speaker, and writer for Atlassian. She is the author of numerous articles published on the Trello and Atlassian blogs and is a regular contributor to various publications on Medium including HackerNoon, Art+Marketing, and PoetsUnlimited. She speaks at tech conferences around the world about agile, breaking down silos, and building empathy.
Get started free with the Jira project management template
Manage activities across any project with powerful task management and easy prioritization tools.
What is agile project management (AMP)?
Agile project management (APM) is an iterative approach to managing and executing projects, particularly in product development.
Agile project management involves breaking down a project into smaller, manageable steps or iterations, which are often called sprints. Each iteration involves a cycle of planning, execution, and evaluation, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changes and continuously improve the product. This approach is incremental and iterative, focusing on collaboration, flexibility, and customer feedback to deliver value throughout the project lifecycle.
Here is everything you need to know to get started or refine your agile project management practices.
A brief history of the agile project management methodology
Stemming from Toyota's lean manufacturing concept of the 1940s, software development teams have embraced agile methodologies to reduce waste and increase transparency, while quickly addressing their customers' ever-changing needs. A stark change from waterfall project management that focuses on "big bang" launches, agile helps software teams collaborate better and innovate faster than ever before.
Traditional agile project management can be categorized into two frameworks: scrum and kanban. While scrum is focused on fixed-length project iterations, kanban is focused on continuous releases. Upon completion, the team immediately moves on to the next.
Agile project management framework 1: Scrum
Scrum is a framework for agile project management that uses fixed-length iterations of work, called sprints. There are four ceremonies that bring structure to each sprint.
It all starts with the backlog, or body of work that needs to be done. In scrum, there are two backlogs: one is the product backlog (owned by the product owner) which is a prioritized list of features, and the other is the sprint backlog which is filled by taking issues from the top of the product backlog until the capacity for the next sprint is reached. Scrum teams have unique roles specific to their stake in the process. Typically there's a scrum master, or champion of the scrum method for the team; the product owner, who's the voice of the product; and the scrum team, who are often cross-functional team members in charge of getting s@#$ done.
The four ceremonies of scrum
Sprint Planning | Sprint Demo | Daily Standup | Retrospective |
A team planning meeting that determines what to complete in the coming sprint. | A sharing meeting where the team shows what they've shipped in that sprint. | Also known as a stand-up, a 15-minute mini-meeting for the software team to sync. | A review of what did and didn't go well with actions to make the next sprint better. |
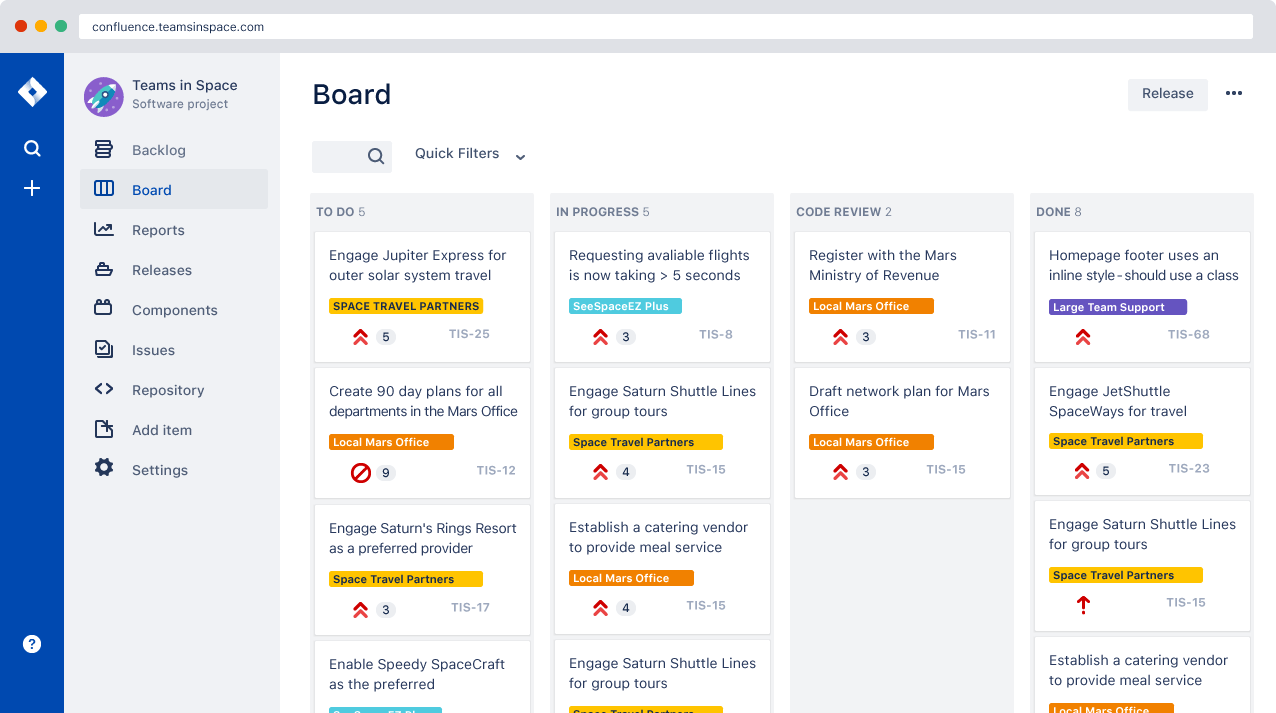
Scrum board example | Atlassian agile coach
Agile project management framework 2: Kanban
Kanban is a framework for agile project management that matches the work to the team's capacity. It's focused on getting things done as fast as possible, giving teams the ability to react to change even faster than scrum.
Unlike scrum, kanban has no backlogs (usually). Instead, work sits in the To Do column. This enables kanban teams to focus on continuous releases, which can be done at any time. All work is visible, scoped, and ready to execute on so that when something is completed, the team immediately moves on to the next. The amount of work is matched to the team's capacity through WIP limits, which is a predefined limit of work that can be in a single column at one time (except the To Do column). The kanban framework includes the following four components:
The four components of kanban
List of work (or stories) | Columns or lanes | Work in Progress Limits (WIP) | Continuous Releases |
List of work, or stories, are defined as issues or tasks that need to get done. | Used on a kanban board to distinguish tasks from different workstreams, users, projects, etc. | A rule to limit the amount of work to be done based on the team's capacity. | The team works on the amount of stories within the WIP limit and can release at anytime. |
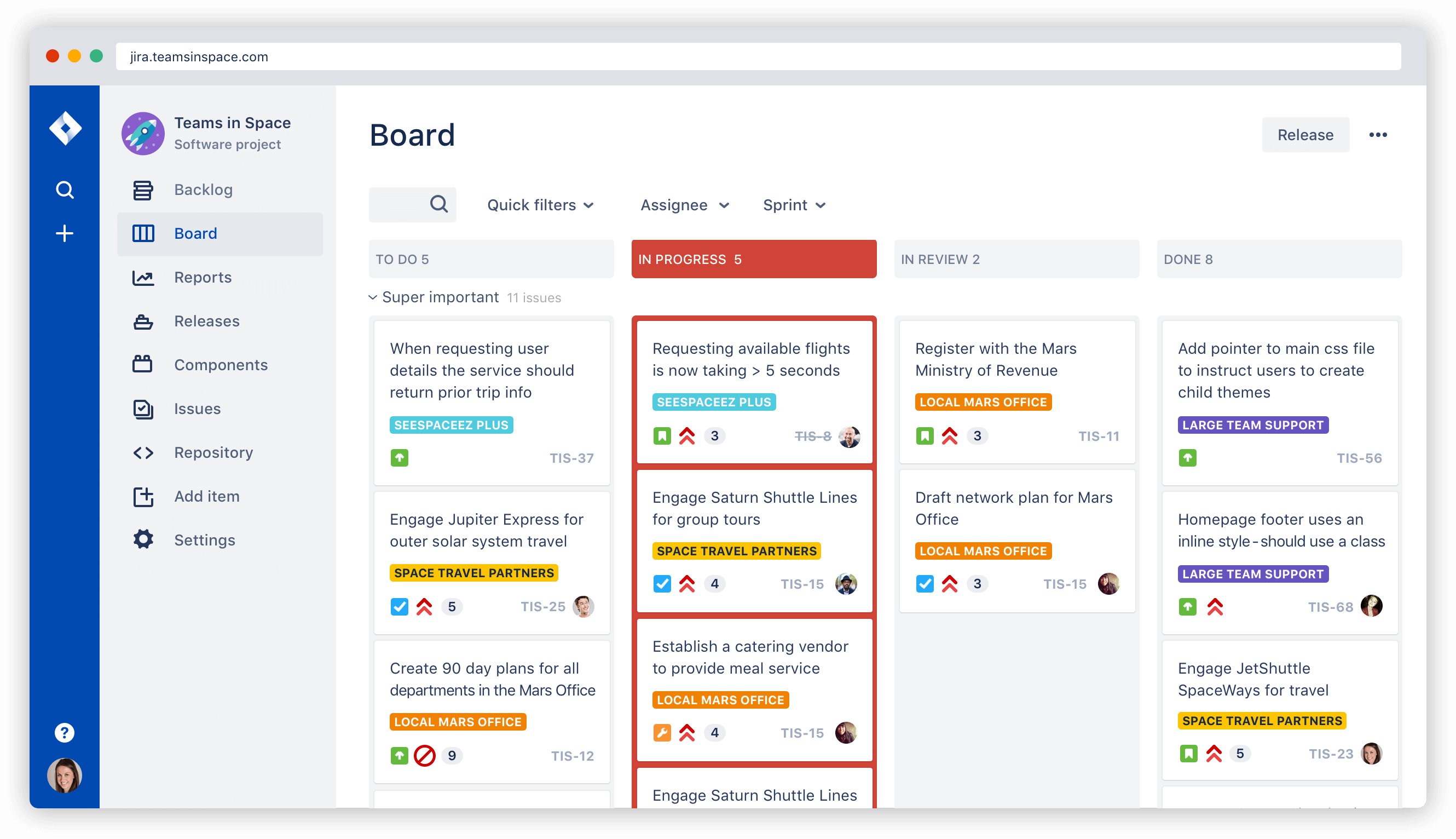
Kanban board example | Atlassian agile coach
Responsibilities of agile project managers
Whatever agile framework you choose to support your software development, you'll need a way to see your team's progress so you can plan for future work or sprints. Agile project estimating helps both scrum and kanban teams understand their capacity. Agile reports show the team's progress over time. Gantt charts and backlog grooming help project managers keep the list of work current and ready for the team to tackle.
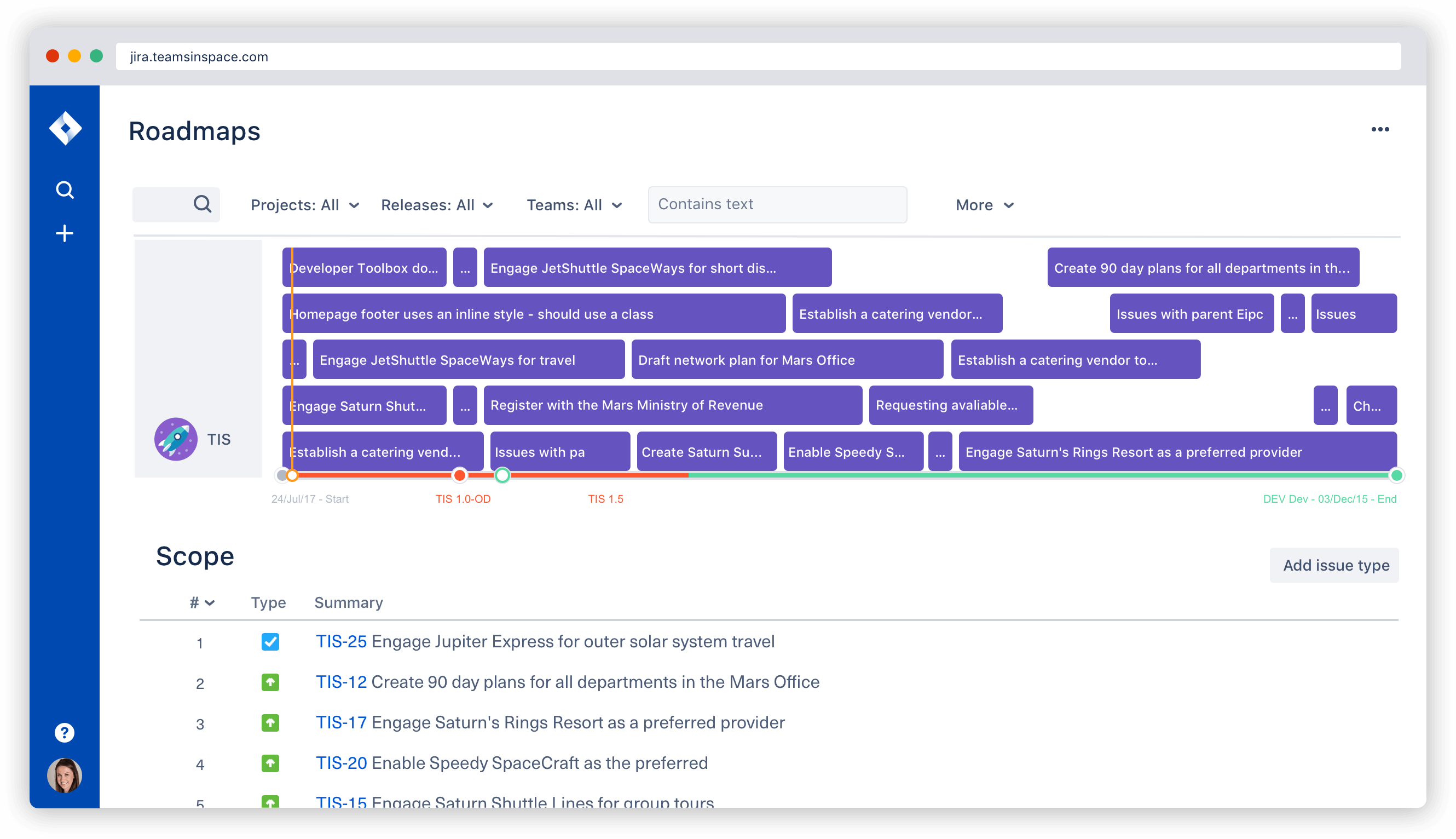
Agile project estimations | Atlassian agile coach
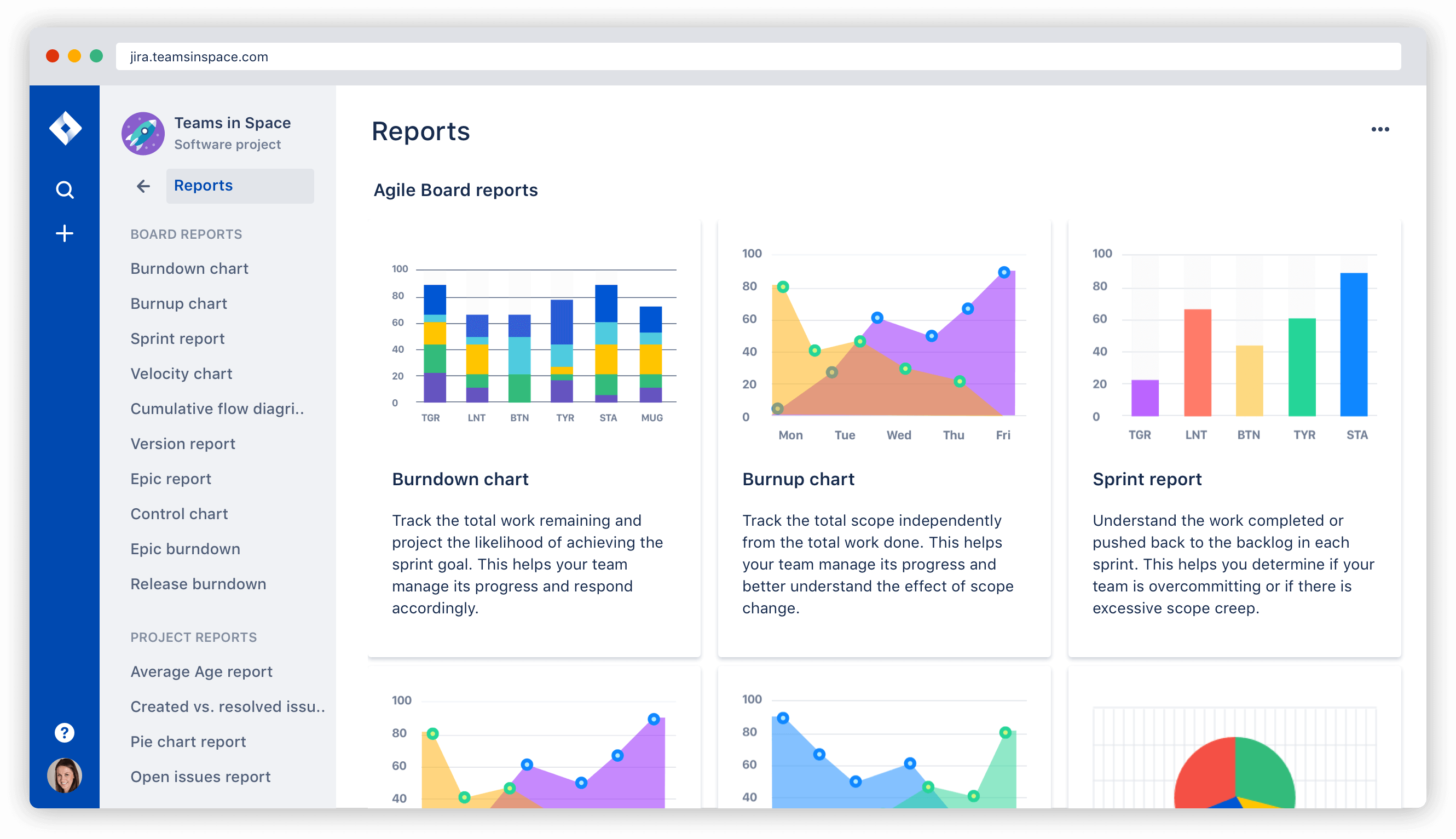
Agile reporting example | Atlassian agile coach

Agile backlog example | Atlassian agile coach
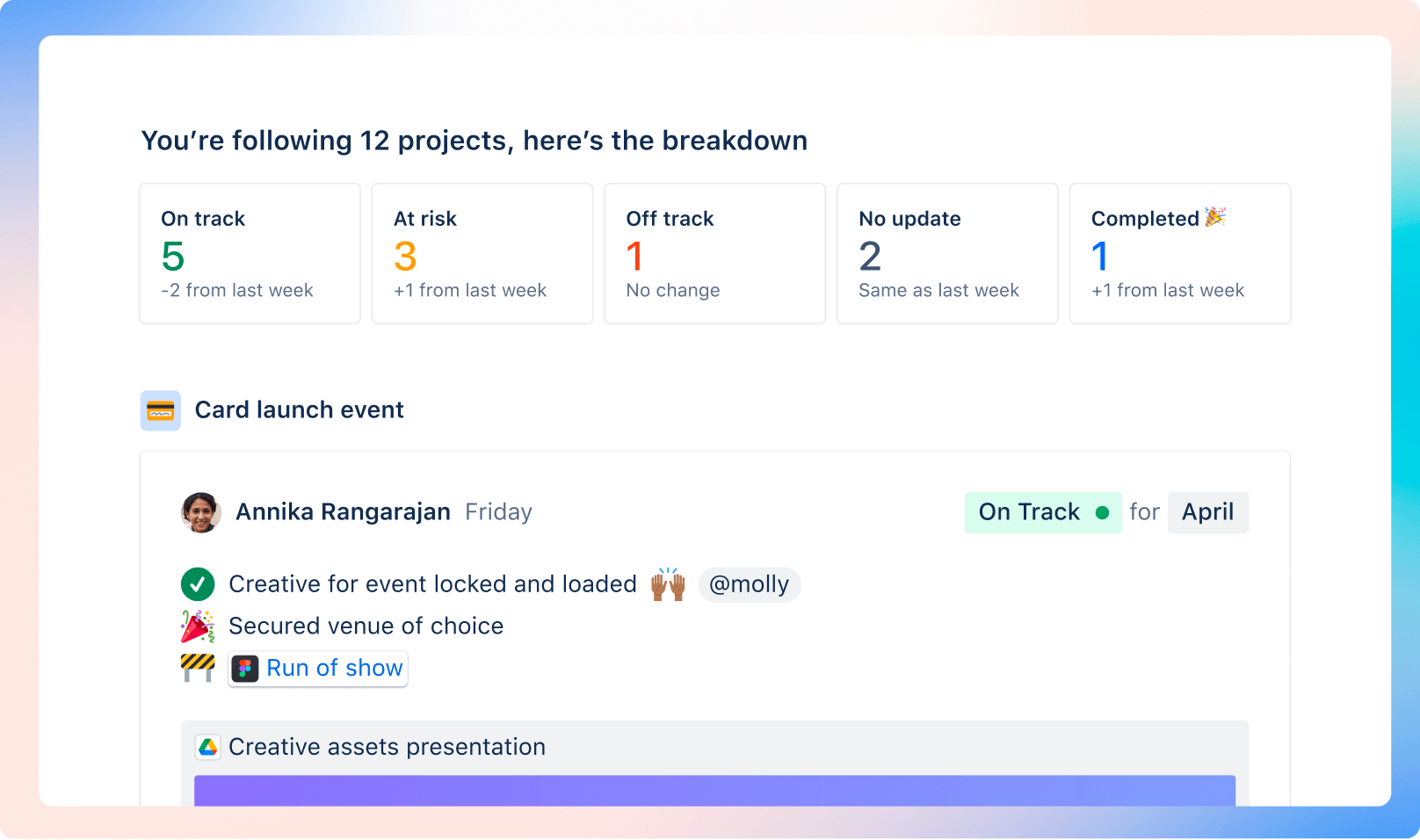
Agile example | effective stakeholder communication
- The Agile Coach
- Agile Manifesto
Agile project management
- Overview
- Project management intro
- Workflow
- Epics, stories, themes
- Epics
- User Stories
- Estimation
- Metrics
- Gantt chart
- Program management vs. project management
- Project baseline
- Continuous improvement
- Lean principles
- 3 pillars of Scrum
- Scrum Board
- Waterfall Methodology
- Velocity in Scrum
- What is Definition of Ready
- Lean vs. agile
- Scrumban
- Lean Methodology
- Sprint backlog
- Burn up chart
- 4 kanban principles
- 4 kanban metrics
- Program vs. Project Manager
- Gantt chart examples
- Definition of done
- Backlog grooming
- Lean process improvement
- Backlog refinement meetings
- Scrum values
- Scope of work
- Scrum tools
- Tools
- Workflow automation software
- Templates
- Task tracker
- Workflow automation
- Status report
- Workflow chart
- Project roadmap
- Project schedule
- Tracking software
- Roadmap tools
- Technology roadmap
- Project scheduling software
- Backlog management tools
- Understanding workflow management strategies
- Workflow examples
- Create project roadmap
- Sprint planning tools
- Sprint demo
- Project Timeline Software
- Top task management tools
- Product backlog vs. sprint backlog
- Top workflow management tools
- Project dependencies
- Task dashboard guide
- Sprint cadence
- Fast tracking
Product Management
- Overview
- Product Roadmaps
- Product Manager
- Tips for new product managers
- Roadmaps
- Tips for presenting product roadmaps
- Requirements
- Product analytics
- Product development
- Remote product management
- Minimal viable product
- Product discovery
- Product specification
- Product development strategy
- Product development software
- New product development process
- Product management KPIs
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Product critique
- Prioritization frameworks
- Product features
- Product management tools
- Product Lifecycle Management
- 9 best roadmap software for teams
- Product launch checklist
- Product strategy
- Product engineering
- Product operations
- Portfolio management
- AI and product management
- Growth product management
- Product metrics
- Product release
- Feature request
- Product launch
- Product planning
- Product launch event
- Value Stream Management
- DevOps
Agile tutorials
- Overview
- Jira and Confluence sprint refinement
- How to do scrum with Jira
- Learn kanban with Jira
- Learn how to use Epics in Jira
- Learn how to create an agile board in Jira
- Learn how to use sprints in Jira
- Learn Versions with Jira
- Learn Issues with Jira
- Learn burndown charts with Jira
- Auto-create sub-tasks and update fields in Jira
- How to automatically assign issues with Jira Automation
- How to sync epics stories with Jira Automation
- Automatically escalate overdue issues in Jira
About the Agile Coach
- All articles
Agile Project Management - What is it and how to get started?
How agile project management can work for your software team

By Claire Drumond
By Claire Drumond
Claire Drumond is a marketing strategist, speaker, and writer for Atlassian. She is the author of numerous articles published on the Trello and Atlassian blogs and is a regular contributor to various publications on Medium including HackerNoon, Art+Marketing, and PoetsUnlimited. She speaks at tech conferences around the world about agile, breaking down silos, and building empathy.
Get started free with the Jira project management template
Manage activities across any project with powerful task management and easy prioritization tools.
What is agile project management (AMP)?
Agile project management (APM) is an iterative approach to managing and executing projects, particularly in product development.
Agile project management involves breaking down a project into smaller, manageable steps or iterations, which are often called sprints. Each iteration involves a cycle of planning, execution, and evaluation, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changes and continuously improve the product. This approach is incremental and iterative, focusing on collaboration, flexibility, and customer feedback to deliver value throughout the project lifecycle.
Here is everything you need to know to get started or refine your agile project management practices.
A brief history of the agile project management methodology
Stemming from Toyota's lean manufacturing concept of the 1940s, software development teams have embraced agile methodologies to reduce waste and increase transparency, while quickly addressing their customers' ever-changing needs. A stark change from waterfall project management that focuses on "big bang" launches, agile helps software teams collaborate better and innovate faster than ever before.
Traditional agile project management can be categorized into two frameworks: scrum and kanban. While scrum is focused on fixed-length project iterations, kanban is focused on continuous releases. Upon completion, the team immediately moves on to the next.
Agile project management framework 1: Scrum
Scrum is a framework for agile project management that uses fixed-length iterations of work, called sprints. There are four ceremonies that bring structure to each sprint.
It all starts with the backlog, or body of work that needs to be done. In scrum, there are two backlogs: one is the product backlog (owned by the product owner) which is a prioritized list of features, and the other is the sprint backlog which is filled by taking issues from the top of the product backlog until the capacity for the next sprint is reached. Scrum teams have unique roles specific to their stake in the process. Typically there's a scrum master, or champion of the scrum method for the team; the product owner, who's the voice of the product; and the scrum team, who are often cross-functional team members in charge of getting s@#$ done.
The four ceremonies of scrum
Sprint Planning | Sprint Demo | Daily Standup | Retrospective |
A team planning meeting that determines what to complete in the coming sprint. | A sharing meeting where the team shows what they've shipped in that sprint. | Also known as a stand-up, a 15-minute mini-meeting for the software team to sync. | A review of what did and didn't go well with actions to make the next sprint better. |

Scrum board example | Atlassian agile coach
Agile project management framework 2: Kanban
Kanban is a framework for agile project management that matches the work to the team's capacity. It's focused on getting things done as fast as possible, giving teams the ability to react to change even faster than scrum.
Unlike scrum, kanban has no backlogs (usually). Instead, work sits in the To Do column. This enables kanban teams to focus on continuous releases, which can be done at any time. All work is visible, scoped, and ready to execute on so that when something is completed, the team immediately moves on to the next. The amount of work is matched to the team's capacity through WIP limits, which is a predefined limit of work that can be in a single column at one time (except the To Do column). The kanban framework includes the following four components:
The four components of kanban
List of work (or stories) | Columns or lanes | Work in Progress Limits (WIP) | Continuous Releases |
List of work, or stories, are defined as issues or tasks that need to get done. | Used on a kanban board to distinguish tasks from different workstreams, users, projects, etc. | A rule to limit the amount of work to be done based on the team's capacity. | The team works on the amount of stories within the WIP limit and can release at anytime. |

Kanban board example | Atlassian agile coach
Responsibilities of agile project managers
Whatever agile framework you choose to support your software development, you'll need a way to see your team's progress so you can plan for future work or sprints. Agile project estimating helps both scrum and kanban teams understand their capacity. Agile reports show the team's progress over time. Gantt charts and backlog grooming help project managers keep the list of work current and ready for the team to tackle.

Agile project estimations | Atlassian agile coach

Agile reporting example | Atlassian agile coach

Agile backlog example | Atlassian agile coach

Agile example | effective stakeholder communication
Recommended for you
Templates
Ready-made Jira templates
Browse our library of custom Jira templates for various teams, departments, and workflows.
Product guide
A comprehensive introduction to Jira
Use this step-by-step guide to discover essential features and the best practices to maximize your productivity.
Git Guide
Understanding the Basics of Git
From beginners to advanced experts, use this guide to Git to learn the basics with helpful tutorials and tips.